bi()
Here are how to use bi() functions.
A.bi()
Description:
Split a low-frequency categorical enumerated sequence variable that contains a number of categories not greater than 6 into multiple binary variables during modeling.
Syntax:
|
A.bi() |
During modeling, split low-frequency categorical enumerated variable A that contains a number of categories not greater than 6 into multiple binary variables, and return a binary sequence consisting of a table sequence of splitting result and a sequence of splitting process records Rec. |
|
A.bi@r(Rec) |
During scoring, split low-frequency categorical enumerated variable A that contains a number of categories not greater than 6 into multiple binary variables according to the sequence of splitting process records Rec, and return result as a table sequence. |
Note:
The external library function (See External Library Guide) splits a low-frequency categorical enumerated sequence variable that contains a number of categories not greater than 6 into multiple binary variables during modeling.
Parameter:
|
A |
A sequence, which is a low-frequency categorical enumerated variable that contains a number of categories no greater than 6. |
|
Rec |
A sequence of splitting process records. |
Return value:
Sequence/Table sequence
Example:
|
|
A |
|
|
1 |
=T("D://house_prices_train.csv") |
|
|
2 |
=A1.(MSZoning) |
A variable containing a number of categories no greater than 6. |
|
3 |
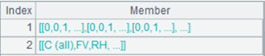
=A2.bi() |
A3(1) A table sequence of splitting result; A3(2) A sequence of splitting process records Rec. |
|
4 |
=A2.bi@r(A3(2)) |
Split A2’s variable into multiple variables according to A3’s sequence of splitting process records Rec. |
P.bi()
Description:
The external library function (See External Library Guide) splits a low-frequency categorical enumerated table sequence/record sequence variable that contains a number of categories not greater than 6 into multiple binary variables during modeling.
Syntax:
|
P.bi(cn) |
During modeling, split low-frequency categorical enumerated variable cn that contains a number of categories not greater than 6 into multiple binary variables, and return a binary sequence consisting of a table sequence of splitting result and a sequence of splitting process records Rec. |
|
P.bi@r(cn, Rec) |
During scoring, split low-frequency categorical enumerated variable cn that contains a number of categories not greater than 6 into multiple binary variables according to the sequence of splitting process records Rec, and return result as a table sequence. |
Parameter:
|
P |
A table sequence/record sequence. |
|
cn |
A string/number, which is the name of column (or the column number starting from 1) – the to-be-pre-processed variable – in a table sequence or record sequence. |
|
Rec |
A sequence of splitting process records. |
Return value:
Sequence/Table sequence
Example:
|
|
A |
|
|
1 |
=T("D://house_prices_train.csv") |
|
|
2 |
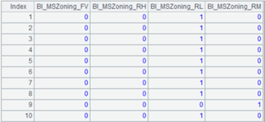
=A1.bi("MSZoning") |
Split variable “MSZoning” into multiple binary variables. A2(1) Splitting result; A2(2) Splitting process records Rec. |
|
3 |
=A1.bi@r("MSZoning",A2(2)) |
Split A1’s variable according to A2’s splitting process records. |