top()
Here’s how to use top() function.
A.top()
Description:
Compute an expression over each member of a sequence and return a sequence consisting of the first n members or values.
Syntax:
|
A.top(n,x) |
Compute expression x over each member of the sequence A, sort the resulting members, and return a sequence consisting of the first n values of x. |
|
A.top(n;x,...) |
Compute expression x,… over each member of the sequence A, sort the resulting members, and return a sequence consisting of the first n members of sequence A. |
|
A.top(n,y,x) |
Compute expression x over each member of the sequence A and then expression y over results of computing expression x, sort values of x according to the values of y, and return a sequence consisting of the first n values of x. |
Note:
The function computes expression x over each member of sequence A, sorts the resulting members, and returns a sequence consisting of the first n members or n values of expression x.
When there are duplicate members in the sequence, use dense ranking by default.
When n>0, return the first n smallest members(values); when n<0, return the first n largest members(values); when n=0, return null. n must not be omitted. The omission of x is equivalent to ~.
Parameter:
|
A |
A sequence. |
|
n |
An integer. |
|
y |
An expression. |
|
x |
An expression. |
Option:
|
@1 |
Return a single value if n is ±1. |
|
@0 |
Do not ignore null members; ignore null members by default. |
|
@r |
Use standard competition ranking, where members having equal values are given equal rank and the next member is given the next highest rank. |
|
@i |
Use dense ranking, where members having equal values are given equal rank and the next members are given the immediately following ranking number. |
Return value:
Sequence
Example:
With syntax A.top(n,x):
|
|
A |
|
|
1 |
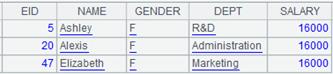
=connect("demo").query("select top 10 NAME,SALARY from employee") |
Return a table sequence:
|
|
2 |
=A1.top(3,SALARY+500) |
Compute expression SALARY+500 over each record of A1’s table sequence, sort the table sequence by the expression’s values, and return a sequence consisting of the first 3 smallest values of the expression:
|
|
3 |
=A1.top(-3,SALARY) |
Sort A1’s table sequence by SALARY, and, as n<0, return a sequence consisting of the first 3 largest SALARY values:
|
|
4 |
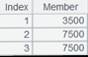
=[2,6,4,12,6,5,2].top(4) |
As parameter x is absent, the function returns the following result:
|
With syntax A.top(n;x,…):
|
|
A |
|
|
1 |
=connect("demo").query("select top 10 NAME,SALARY from employee") |
Return a table sequence:
|
|
2 |
=A1.top(3;SALARY+500) |
Compute expression SALARY+500 over each record of A1’s table sequence, sort the table sequence by the expression’s values, and return a sequence consisting of A1’s records corresponding to the first 3 smallest values of the expression:
|
|
3 |
=A1.top(-6;DEPT,SALARY) |
Sort A1’s table sequence by DEPT and SALARY, and return a sequence consisting of A1’s records corresponding to the first 6 largest values of the two fields:
|
With syntax A.top(n,y,x):
|
|
A |
|
|
1 |
[21,3,12,5] |
|
|
2 |
=A1.top(3,~%10,~+6) |
First, compute expression x ~+6 over each member of A1’s sequence and get [27,9,18,11] as the expression’s result; then compute expression y ~%10 over x’s result and get [7,9,8,1] as y’s result; and finally return a sequence consisting of values of x corresponding to the first 3 smallest values of y; below is the result sequence:
|
|
3 |
=A1.top(-3,~%10,~+6) |
As parameter n is -3, the function returns a sequence consisting of values of x corresponding to the first 3 largest values of y; below is the result sequence:
|
Use @1 option and return a single value when n is ±1:
|
|
A |
|
|
1 |
=[2,6,4,12,6,5] |
|
|
2 |
=A1.top(1) |
Return a sequence made up of the one smallest value:
|
|
3 |
=A1.top@1(1) |
With @1 option and as parameter n is 1, the function returns the smallest value among members of A1’s sequence:
|
|
4 |
=A1.top@1(-1) |
With @1 option and as parameter n is -1, the function returns the largest value among members of A1’s sequence:
|
Do not ignore nulls when @0 option is used:
|
|
A |
|
|
1 |
=[5,7,2,null,3] |
|
|
2 |
=A1.top(3) |
Get the first 3 smallest member values in the sequence, during which the null member is by default ignored:
|
|
3 |
=A1.top@0(3) |
As @0 option is present, the null member is also counted:
|
Use different ranking types to display result of ranking a sequence having duplicate values when @r/@i option is present:
|
|
A |
|
|
1 |
[a,b,e,b,d,a,c,c,b] |
Return a sequence having duplicate members. |
|
2 |
=A1.top(3) |
Use dense ranking by default and get the first 3 smallest values:
|
|
3 |
=A1.top@r(3) |
Use standard competition ranking as @r option works – the member after the two members having the same ranking is given the next highest rank, which is equivalent to a ranking [1,1,3,3,3,6,6,8,9] when members are sorted; below is the return result:
|
|
4 |
=A1.top@i(3) |
Use dense ranking as @i option works – members after the two members having the same ranking are given immediately following ranking numbers, which is equivalent to a ranking [1,1,2,2,2,3,3,4,5] when members are sorted; below is the return result:
|
Related function: