get()
Description:
Get information about base members at a superior level in a multilevel loop function.
Syntax:
get(level,F;a:b)
Note:
The function, only valid with a loop function, gets information about base members at a superior level in a multilevel loop function.
Parameter:
|
level |
The number of levels between the current level, which is recorded as 0, and the desired superior level. |
|
F |
Field name, which is sometimes represented by #, denoting the sequence number of a field; get members directly when it is absent. |
|
a:b |
An offset interval, where a and b are offset values for members’ sequence numbers; default a is 1-#, and default b is ~.len() - # ; can be omitted. |
Return value:
A member value in a sequence or a sequence of values.
Example:
|
|
A |
|
|
1 |
[1,2,3] |
|
|
2 |
=A1.() |
Return members of A1.
|
|
3 |
=A1.(A1.(get(0))) |
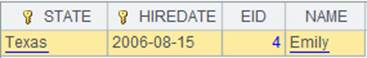
Use a two-level loop function to compute A1; the get() function gets information of base members in the current level because parameter level’s value is 0; the whole operation is equivalent to computing expression A1.(A1.()), and returns the following result:
|
|
4 |
=A1.(A1.(get(1))) |
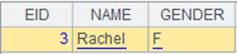
Return information of base members in the level above the current loop level; below is the result:
|
|
5 |
=A1.(A1.(get(1;-1))) |
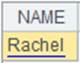
Return information of base members in the level above the current loop level; as parameter a’s value is -1, information of the previous base member is returned; below is the result:
|
|
6 |
=A1.(A1.(get(1;-1:1))) |
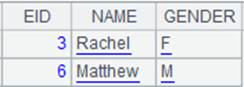
In the get() function, parameter level’s value is 1, parameter a’s value is -1 and parameter b’s value is 1; the whole operation returns information of base members from the previous to the next of the member in the above level of the current loop level; below is the result:
|
|
|
A |
|
|
1 |
=[2,3,8] |
|
|
2 |
=A1.(A1.(abs(~-get(1)))) |
Compute differences of each member in sequence A1 and the other members (including the current member itself), and gets the following result:
|
|
3 |
=A1.(A1.max(abs(~-get(1)))) |
Compute the maximum difference between each member in sequence A1 and the other members (including the current member itself), and gets the following result:
|