E()
Description:
Convert a string, two-layer sequence, table sequence, record sequence or a single value to a specific type.
Syntax:
E(x)
Note:
When parameter x is a two-layer sequence, convert it to a multi-row table sequence where each row is a record and the first row holds column headers;
When parameter x is a string of rows separated by carriage return or a string of tab-separated columns, split them before conversion;
Convert to a two-layer sequence when parameter x is a table sequence or a record sequence.
Parameter:
|
x |
A sequence/string/table sequence/record sequence/single value |
Option:
|
@b |
Do not use headers |
|
@p |
Transpose a result two-layer sequence |
|
@s |
Return a string separated by carriage return or tab when parameter x is a table sequence |
|
@1 |
Convert to a single-layer sequence; return a single-layer sequence when parameter x is a single value, and concatenation of members of the sequence when parameter x is a two-layer sequence |
|
@2 |
Return a two-layer sequence when parameter x is a single value |
Return value:
A table sequence, a sequence or a string
Example:
|
|
A |
|
|
1 |
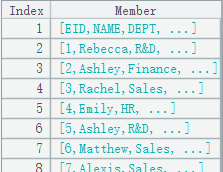
=connect("demo").query("select EID,NAME,DEPT,SALARY,HIREDATE from EMPLOYEE ") |
|
|
2 |
=E@s(A1) |
Return a string separated by carriage return or tab:
|
|
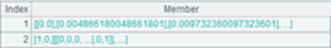
3 |
=E(A2) |
|
|
4 |
=E@b(A3) |
|
|
5 |
=E@1(123) |
Use @1 option to convert a single value to a single-layer sequence, and return [123] |
|
6 |
=E@1([[11,22],[33,44]]) |
Use @1 option to return the concatenation of members of of a two-layer-sequence; the result is [11,22,33,44] |
|
7 |
=E@2(123) |
Use @2 option to convert a single value to a two-layer sequence, and return [[123]] |
Use @p option to transpose a two-layer sequence:
|
|
A |
|
|
1 |
=E@bp([[1,4,5,6],["Emily","Ashley","Kuki","Lily"]]) |
@p option works to transpose the two-layer sequence:
|
|
2 |
=connect("demo").query("select top 5 EID,NAME,SALARY from employee") |
Return a table sequence:
|
|
3 |
=E@p(A2) |
Convert A2 to a two-layer sequence, which, as @p option is present, is transposed:
|