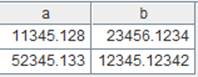
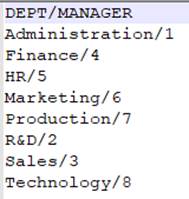
create()
Here’s how to use create() functions.
create ()
Description:
Create an empty table sequence.
Syntax:
create(Fi,…)
Note:
The function creates an empty table sequence taking Fi,… as its fields.
Parameter:
|
Fi |
Field name |
Return value:
An empty table sequence
Example:
|
|
A |
|
|
1 |
=create(id,name,gender) |
|
create(#Fi,…)
Description:
Create an empty table sequence with one or more keys set.
Syntax:
create(#Fi,…)
Note:
The function creates an empty table sequence consisting of fields Fi,…. A field name headed by a hash (#) is a key. For the time being, the function cannot generate a time key directly.
Parameter:
|
Fi |
Field name |
Return value:
Empty table sequence
Example:
|
|
A |
|
|
1 |
=create(#id,#name,gender) |
id field and name field are keys. |
f.create( C,…; x;b )
Description:
Create a composite table based on a file.
f.create(C,…;x;b)
Note:
The function creates a composite table using composite table file f and generates a multizone composite table if f is a homo-name files group. Parameter C is a column, which is a dimension if it is preceded by #, of the would-be composite table, and parameter x is a zone table expression. The dimension and all fields before it must be ordered.
Parameter:
|
f |
A composite table file object or a homo-name files group object |
|
C |
A column of the would-be composite table |
|
x |
A zone table expression, whose result is the integer representing the corresponding zone table |
|
b |
Block size, whose unit is byte. Default value is the “Composite table block size” configured in the configuration options; when esProc is integrated into a third-party application, the parameter’s default value is value of blockSize configured in raqsoftConfig.xml file |
Option:
|
@u |
Do not compress the file; default is to compress it |
|
@r |
Generate a row-wise file while default is columnar storage, which does not support the multicursor |
|
@y |
Force to re-create the file even if the target file already exists; defalut is to terminate computation |
|
@p |
Use the first field as the grouping key |
|
@v |
When columnar storage is used to generate the composite table, check whether each of its columns is pure during data maintenance and save the data type |
|
@t |
Create key for the composite table (including multizone composite table) using dimensions and the last key field is the time key; in this case no attached table is allowed |
|
@d |
Used on a multizone composite table; the first field after key fields is regarded as the update mark field, whose values fall in three types: null representing to-be-added, true representing to-be-deleted, and false meaning to-be-modified; the program retrieves data from a multizone composite table according to the update mark field valuep |
Return value:
A composite table or a homo-name files group
Example:
|
|
A |
|
|
1 |
=file("employee1.ctx") |
Generate composite table file employee1.ctx. |
|
2 |
=A1.create(#EID,NAME,GENDER) |
Create A1’s base table whose columns are EID, NAME and GENDER; EID is the dimension. |
|
3 |
=connect("demo").cursor("select EID,NAME,GENDER,SALARY from employee where GENDER='M' ").sortx(EID) |
|
|
4 |
=connect("demo").cursor("select EID,NAME,GENDER,SALARY from employee where GENDER='F' ").sortx(EID) |
|
|
5 |
=[A3,A4].mcursor() |
Return a multicursor. |
|
6 |
=file("emp.ctx":[1,2]) |
Generate a homo-name files group, which contains two files 1.emp.ctx and 2.emp.ctx. |
|
7 |
=A6.create@y(#EID,NAME,GENDER,SALARY;if(GENDER=="F",1,2)) |
Create a multizone composite table; if(GENDER=="F",1,2) is zone table expression and @y forces to re-create the target file even if it already exists. |
|
8 |
=A7.append@i(A5) |
Append data in A5’s multicursor to A7’s multizone composite table; each part of the multicursor uniquely corresponds to A7’s one zone table. |
|
9 |
=file("1.emp.ctx").open().cursor().fetch() |
View data in zone table 1.emp.ctx. |
|
10 |
=file("2.emp.ctx").open().cursor().fetch() |
View data in zone table 2.emp.ctx. |
Use the first field as the segmentation key:
|
|
A |
|
|
1 |
=file("CITIES.ctx") |
Generate composite table file CITIES.ctx. |
|
2 |
=A1.create@p(STATEID,#CID,NAME,POPULATION) |
Create the base table of CITIES.ctx and use @p option to make the first field STATEID the grouping key; when the option is absent, use dimension field CID as the default grouping field. |
Set the time key:
|
|
A |
|
|
1 |
=file("transaction.ctx") |
|
|
2 |
=A1.create@yt(#UID,#Time,Change,Amount) |
Create the composite table’s base table; @t option works to set UID as the basic key and Time as the time key. |
|
3 |
=file("transaction.txt").cursor@t().sortx(UID,Time) |
Return a cursor ordered by UID and Time. |
|
4 |
=A2.append@i(A3) |
Append cursor A3’s data to the base table. |
|
5 |
=A2.import() |
Retrieve data of the base table.
|
When update mark field is present:
|
|
A |
|
|
1 |
=connect("demo").cursor("select EID,NAME,GENDER from employee") |
|
|
2 |
=A1.derive(null:Defiled) |
|
|
3 |
=A2.new(EID,Defiled,NAME,GENDER) |
Return a cursor, whose content is as follows:
|
|
4 |
=file("ed.ctx":[1,2]) |
Homo-name files group: 1.ed.ctx and 2.ed.ctx. |
|
5 |
=A4.create@yd(#EID,Defiled,NAME,GENDER;if(GENDER=="F",1,2)) |
Create a composite table, set EID as the key, use @d option to make Defield field the deletion mark, and put records where GENDER is F to 1.ed.ctx and the other records to 2.ed.ctx. |
|
6 |
=A5.append@ix(A3) |
Append cursor A1’s data to the multizone composite table. |
|
7 |
=create(EID,Defiled,NAME,GENDER).record([1,true,,2,false, "ABC","F"]).cursor() |
Return a cursor, whose content is as follows:
|
|
8 |
=file("ed.ctx":[3]) |
|
|
9 |
=A8.create@yd(#EID,Defiled,NAME,GENDER;3) |
Add zone table 3.ed.ctx |
|
10 |
=A9.append@i(A7) |
Append cursor A7’s data to zone table 3.ed.ctx. |
|
11 |
=file("ed.ctx":[1,2,3]) |
|
|
12 |
=A11.open() |
Open A11’s multizone composite table. |
|
13 |
=A12.cursor@w() |
Return the multizone composite table as a cursor, use @w option to handle the update mark, which means the record where EID field value is 1 recognized as the to-be-deleted and the one where EID is 2 is recognized as to-be-modified. |
|
14 |
=A13.fetch() |
Fetch data in cursor A13.
We can see that the record where EID is 1 isn’t retrieved from the multizone composite table and NAME value of the one where EID is 2 is modified. |
P.create()
Description:
Generate a new empty table sequence by copying data structure of a specific record sequence.
Syntax:
P.create()
Note:
If parameter P has the key, just copy it.
Parameter:
|
P |
A record sequence |
Return value:
Empty table sequence
Example:
Generated from a record sequence:
|
|
A |
|
|
1 |
=demo.query("select top 1 * from DEPARTMENT") |
|
|
2 |
=A1.to() |
Generate a record sequence. |
|
3 |
=A2.create() |
Create an empty table sequence that has same data structure as A2’s. |
When there is the key:
|
|
A |
|
|
1 |
=demo.query("select top 1 * from DEPARTMENT ") |
|
|
2 |
=A1.keys(DEPT) |
|
|
3 |
=A1.to() |
Generate a record sequence CITIES.ctx. |
|
4 |
=A3.create() |
Create an empty table sequence that has same data structure as A3’s while copying the key. |
T.create ()
Description:
Create an empty table sequence by duplicating data structure of a specific table sequence.
Syntax:
T.create()
Note:
If table sequence T has a key, then duplicate the key at the same time.
Parameter:
|
T |
A table sequence |
Return value:
A new empty table sequence
Example:
Created from a normal table sequence :
|
|
A |
|
|
1 |
=demo.query("select top 1 * from DEPARTMENT") |
|
|
2 |
=A1.create() |
Create an empty table of same structure as A1. |
Copy the key
|
|
A |
|
|
1 |
=demo.query("select * from DEPARTMENT ") |
|
|
2 |
=A1.keys(DEPT) |
|
|
3 |
=A1.create() |
Create an empty table sequence that has not only the same data structure, but also the same key, as table sequence A1. |
T.create(f:b;x)
Description:
Create a new composite table file using the data structure of an existing composite table.
Syntax:
T.create(f:b;x)
Note:
The function creates a new composite table file f using table structure of composite table T, and generates a multizone composite table file when the target f is a homo-name files group. f will include T’s attached tables.
Parameter:
|
T |
A composite table |
|
f |
A composite table file or a homo-name files group |
|
b |
Block size, whose unit is byte and whose default value is 【composite table block size】configured through menu option; when esProc is integrated in the third-party application, use blockSize value configured in raqsoftConfig.xml by default |
|
x |
An integer, which is zone table expression |
Option:
|
@u |
Do not compress data; use compression by default |
|
@r |
Generate a row-oriented file while by default generate a column-oriented one; a row-oriented composite table cannot use multicursor; do not compress a row-oriented file |
|
@y |
Forcibly to create the file even if a namesake one already exists; by default terminate the computation |
Return value:
Composite table
Example:
|
|
A |
|
|
1 |
=create(k1,v1).record([1,10,2,20]).cursor() |
Return a cursor that has data as follows:
|
|
2 |
=create(k1,k2,v2).record([1,11,111,2,22,222]).cursor() |
Return a cursor that has data as follows:
|
|
3 |
=file("ctb.ctx").open() |
Open a composite table file that contains an attached table table2. |
|
4 |
=A3.create@y(file("ctbCp.ctx")) |
Create new composite table file ctbCp.ctx, as well as its attached table, using data structure of composite table ctb.ctx; as @y works, forcibly create the file even if ctbCp.ctx already exists. |
|
5 |
=A4.append@i(A1) |
Append data of A1’s cursor to the base table of composite table ctbCp.ctx. |
|
6 |
=A4.attach(table2) |
Open A4’s attached table table2. |
|
7 |
=A6.append@i(A2) |
Append data of A2’s cursor to ctbCp.ctx’s attached table table2. |
Use @u option to not to compress the generated composite table file:
|
|
A |
|
|
1 |
=file("em.ctx").open() |
Open composite table file em.ctx. |
|
2 |
=A1.create@yu(file("ctbCp2.ctx")) |
Create a non-compressed composite table file ctbCp2.ctx using the existing composite table file em.ctx. |
|
3 |
=file("ctbCp2.ctx").structure() |
View structure of the composite table file ctbCp2.ctx; the false zip value means non-compression:
|
Use @r option to generate a row-oriented file:
|
|
A |
|
|
1 |
=file("em.ctx").open() |
Open composite table file em.ctx. |
|
2 |
=A1.create@yr(file("ctbCp3.ctx")) |
Create a row-oriented composite table file ctbCp3.ctx using the existing composite table file em.ctx. |
|
3 |
=file("ctbCp3.ctx").structure() |
View structure of the composite table file ctbCp3.ctx; the true row value represents row-oriented file:
|
r.create()
Description:
Create a table sequence by copying the data structure of a specified record.
Syntax:
r.create()
Note:
If there’s a key defined in record r, then copy the key at the same time.
Parameter:
|
r |
A record |
Return value:
Empty table sequence
Example:
Generate an empty table sequence from an average record:
|
|
A |
|
|
1 |
=demo.query("select top 1 * from DEPARTMENT") |
|
|
2 |
=A1(1).create() |
Create an empty table of same structure as A1(1) . |
Generate an empty table sequence from a record with the key:
|
|
A |
|
|
1 |
=demo.query("select * from DEPARTMENT ") |
|
|
2 |
=A1.keys(DEPT) |
|
|
3 |
=A1(1).create() |
Generate an empty table sequence by copying the data structure of the record A1(1) and the key . |