sortx()
Here’s how to use sortx() function.
ch.sortx()
Description:
Sort records in a channel.
Syntax:
ch.sortx(x,…)
Note:
The function sorts records in channel ch by expression x,… and returns the sorted records as a channel. This is a function for directly getting a result set from the channel.
Parameter:
|
ch |
Channel |
|
x |
An expression, according to which the records in a given channel is sorted in ascending order |
Return value:
Channel
Example:
|
|
A |
|
|
1 |
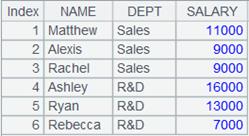
=demo.cursor("select EID,NAME,DEPT,SALARY from EMPLOYEE order by EID desc") |
Return a cursor with desired records. |
|
2 |
=channel() |
Create a channel. |
|
3 |
=A2.sortx(SALARY,EID) |
Sort records in the channel by SALARY field and EID field. |
|
4 |
=A1.push(A2) |
Push data in A1’s cursor into the channel |
|
5 |
=A1.fetch() |
Fetch data from A1’s cursor. |
|
6 |
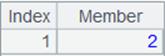
=A2.result() |
Return result as a cursor. |
|
7 |
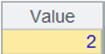
=A6.fetch() |
|
cs.sortx()
Description:
Sort data of a cursor.
Syntax:
cs.sortx(x,…;n)
Note:
The function sorts cursor cs by expression x, and returns result as a cursor. The cursor the function returns is irreversible.
Parameter:
|
cs |
A cursor |
|
x |
An expression to sort members of cursor cs in ascending order |
|
n |
Number of buffer rows; if the number of groups reaches n, write the grouping result to a temporary file; its value will be n times of the default if it is less than 1; by default, esProc will auto-compute the value |
Option:
|
@0 |
Put records with null values at the end; @0 and @n can’t work together |
|
@n |
It can only be used to make the calculation faster when the value of expression x is a positive integer over which group of records can be directly numbered. @0 and @n can’t work together |
|
@g |
Treat parameter n as the segmentation expression by which records are first segmented and then grouped and sorted |
Return value:
Cursor
Example:
|
|
A |
|
|
1 |
=demo.cursor("select NAME,BIRTHDAY,HIREDATE from Employee") |
Return retrieved data as a cursor. |
|
2 |
=A1.sortx(BIRTHDAY) |
Sort the cursor’s BIRTHDAY field. |
|
3 |
=A2.fetch() |
Retrieve data from cursor A2. |
|
4 |
=demo.cursor("select * from DEPT") |
Return retrieved data as a cursor. |
|
5 |
=A4.sortx@0(FATHER).fetch() |
Sort records in the cursor by FATHER field and put the one with null value at the end. |
|
6 |
=A4.sortx@g(DEPTID;FATHER==12).fetch() |
Group records according to whether FATHER value is 12 and then sort each group by DEPTID. |
|
7 |
=A1.sortx(BIRTHDAY;2) |
Sort BIRTHDAY field in the cursor; since data is divided into two groups to be processed, write the grouping result to a temporary file. |
|
8 |
=demo.cursor("select * from SCORES") |
|
|
9 |
=A8.sortx@n(SCORE).fetch() |
The result of fetching SCORE values are integers; here @n option is used to speed up the sorting. |
Related function:
cs.sortx()
Description:
Sort a cluster cursor.
Syntax:
cs.sortx(x,…;n)
Note:
The function sorts cluster cursor cs by expression x and returns a cluster cursor.
Option:
|
@c |
Won’t merge result sets returned by the nodes but return a cluster cursor segmented in the same way |
Parameter:
|
cs |
A cluster cursor |
|
x |
An expression by which records in a specified cluster cursor are sorted in ascending order |
|
n
|
Number of buffer rows; if the number of groups reaches n, write the grouping result to a temporary file; its value will be n times of the default if it is less than 1; by default, esProc will auto-compute the value |
Return value:
A cluster cursor
Example:
|
|
A |
|
|
1 |
[192.168.0.110:8281,192.168.18.143:8281] |
|
|
2 |
=file("emp.ctx", A1) |
|
|
3 |
=A2.open() |
Open a cluster composite table file. |
|
4 |
=A3.cursor() |
Return a cluster cursor. |
|
5 |
=A4.sortx(EID) |
Sort A4’s cluster cursor by EID and return result also as a cluster cursor. |
f.sortx()
Description:
Sort a bin file or a sequence of bin files and generate a new bin file.
Syntax:
|
f.sortx(Fi,…;fn) |
Sort a bin file according to field Fi and generate a new bin file |
|
[fi,…].sortx(Fi,…;fn) |
Sort a sequence of bin files according to field Fi and generate a new bin file; perform a simple concatenation when parameter Fi is absent |
Note:
The function sorts bin file f or a sequence of bin files [fi,…] by certain field Fi , generates a new bin file fn and return non-null if the operation succeeds.
Parameter:
|
f |
A bin file object |
|
[fi,…] |
A sequence of bin files of same structure |
|
Fi |
Name(s) of f field(s) by which the file is sorted |
|
fn |
Bin file object(s); generate a temporary file and return its cursor when this parameter is absent |
Option:
|
@z |
Sort in descending order; default is ascending |
Return value:
Boolean/cursor
Example:
Sort a bin file:
|
|
A |
|
|
1 |
=file("PERFORMANCE.btx") |
A bin file object; its content is as follows:
|
|
2 |
=file("PER-cp.btx") |
Specify a bin file object. |
|
3 |
=A1.sortx(BONUS;A2) |
Sort PERFORMANCE.btx by BONUS field and generate a new bin file PER-cp.btx, whose content is as follows:
|
|
4 |
=A1.sortx(BONUS) |
As parameter fn is absent, generate a temporary file in the temporary directory and return a cursor, whose content is same as that in A3. |
|
5 |
=A1.sortx@z(BONUS) |
Sort by BONUS field in descending order and return a cursor whose content is as follows:
|
Sort a sequence of bin files:
|
|
A |
|
|
1 |
=file("f_emp.btx") |
A bin file object; its content is as follows:
|
|
2 |
=file("m_emp.btx") |
A bin file object; its content is as follows:
|
|
3 |
=file("emp_all.btx") |
|
|
4 |
=[A1,A2].sortx(SALARY,EID;A3) |
Sort f_emp.btx and m_emp.btx by SALARY and EID fields and generate a new bin file emp_all.btx, whose content is as follows:
|
|
5 |
=[A1,A2].sortx(SALARY) |
As parameter fn is absent, return a cursor. |
Perform a simple concatenation on a sequence of bine files when parameter Fi is absent:
|
|
A |
|
|
1 |
=file("f_emp.btx") |
A bin file object whose content is as follows:
|
|
2 |
=file("m_emp.btx") |
A bin file object whose content is as follows:
|
|
3 |
=file("emp_gb.btx") |
|
|
4 |
=[A1,A2].sortx(;A3) |
Concatenate f_emp.btx and m_emp.btx and generate a new bin file emp_gb.btx whose content is as follows:
|