write()
Here’s how to use write() function.
f. write()
Description:
Write a string or a sequence into a file.
Syntax:
|
f.write(s) |
|
|
f.write(A) |
Write A, the sequence of strings to file f; each member occupies one row |
Note:
The original file will get overwritten, meaning the contents in the file f will be replaced with the string s or the string sequence A.
Parameter:
|
s |
A string |
|
f |
A file |
|
A |
A string sequence |
Option:
|
@a |
Append data into a file, instead of overwriting it. If the file has contents before appending, then start a new line (with carriage return) to append |
|
@b |
Write as a binary file without using the carriage return automatically |
|
@w |
Use Windows-style \r\n line break; by default, the line break is specified by OS |
Example:
|
|
A |
|
|
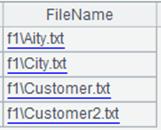
1 |
=file("D:/tmp.txt") |
|
|
2 |
>A1.write("China") |
|
|
3 |
>A1.write@a("Chinese") |
|
|
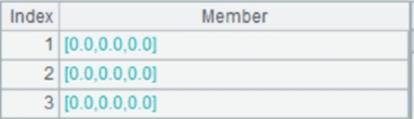
4 |
=["China","America","England "] |
|
|
5 |
>A1.write(A4) |
|
|
6 |
>A1.write(string(now())+":start") |
Use the write@a function to compose a log. |
|
7 |
>A1.write@a(string(now())+":end") |
|
|
8 |
>A1.write@a(string(now())+":startPrint") |
|
|
9 |
>A1.write@a(string(now())+":endPrint") |
|
|
10 |
=file("D:/test.btx") |
A text file with binary data. |
|
11 |
=file("D:/result.btx") |
|
|
12 |
=A10.read@b() |
Read in test.bxt in string format. |
|
13 |
=A11.write@b(A12) |
Generate result.btx in binary format. |
|
14 |
=file("D:/employee.txt").write@w(A4) |
Use Windows-style \r\n line break. |
Related function: