T.fjoin ()
Description:
Define a foreign-key-style association on a pseudo table and return a new pseudo table.
Sytnax:
T.fjoin(w:Ti,x:F,…;…)
Note:
The function defines a computation on pseudo table T, which will first compute expression w and then expression x over each of its rows, make results of x values of the new field F to be joined into pseudo table T, and returns a new pseudo table.
Ti is w’s alias, which can be referenced in expression x; when x is represented by ~, it is treated as w; re-assign field F when it already exists in pseudo table sequence T.
A primary table and a subtable can be associated through the foreign key in parameter w.
Parameter:
|
T |
A pseudo table |
|
w |
An expression, which, besides the regular syntax, can be used in the following syntax: 1. K=w, which means value assignment; K is a field of pseudo table T, and you can use an esProc function in w; 2. (Ki=wi,…,w), which contains the combined use of Ki=wi, where w is a logical expression, and where Ki can be referenced in w |
|
Ti |
Alias of expression w; can be absent |
|
x |
An expression; can be absent |
|
F |
Field name in expression x; can be absent |
Return value:
Pseudo table
Option:
|
@i |
Delete the current record when result of expression w is null or false |
Example:
When using syntax K=w:
|
|
A |
|
|
1 |
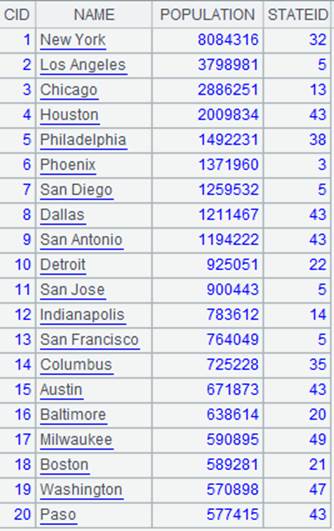
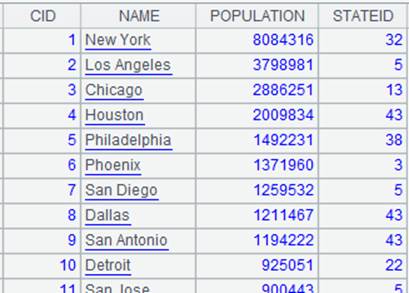
=create(file).record(["cities-x.ctx"]) |
Below is content of composite table cities-x.ctx:
|
|
2 |
=pseudo(A1) |
Generate a pseudo table from the composite table |
|
3 |
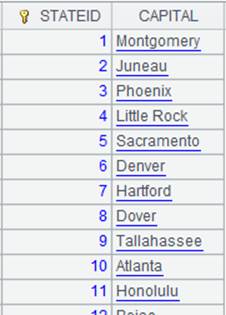
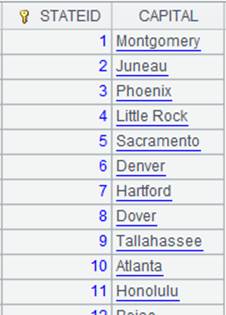
=connect("demo").query("SELECT top 20 * FROM STATECAPITAL").keys(STATEID) |
Return a table sequence whose primary key is STATEID
|
|
4 |
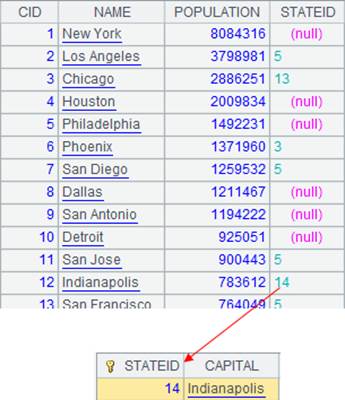
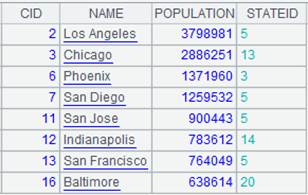
=A2.fjoin(STATEID=A3.find(STATEID)) |
Define a computation on A2’s pseudo table, which will use syntax k=w to associate table sequence A3 and pseudo table A2 through the latter’s foreign key STATEID, assign corresponding referencing records in A3 to A2’s foreign key and nulls to the non-matching records, and return a new pseudo table:
|
|
5 |
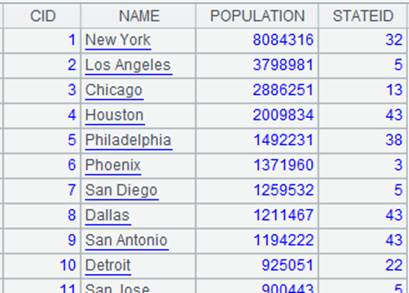
=A4.import() |
Import data from A4’s pseudo table while the computation defined on A2’s pseudo table in A4 is executed, and return the following pseudo table:
|
When @i option is present:
|
|
A |
|
|
1 |
=create(file).record(["cities-x.ctx"]) |
Below is content of composite table cities-x.ctx:
|
|
2 |
=pseudo(A1) |
Generate a pseudo table from the composite table |
|
3 |
=connect("demo").query("SELECT top 20 * FROM STATECAPITAL").keys(STATEID) |
Return a table sequence whose primary key is STATEID
|
|
4 |
=A2.fjoin@i(STATEID=A3.find(STATEID)) |
Define a computation on A2’s pseudo table, which will use @i option to associate table A3 and A2 through the latter’s foreign key STATEID, where whole records of A2 will be deleted if the foreign key value cannot find a match in A3, and return a new pseudo table.
|
|
5 |
=A4.cursor().fetch() |
Import data from A4’s pseudo table while the computation defined on A2’s pseudo table in A4 is executed, and return the following pseudo table:
|
When using syntax (Ki=wi,…,w):
|
|
A |
|
|
1 |
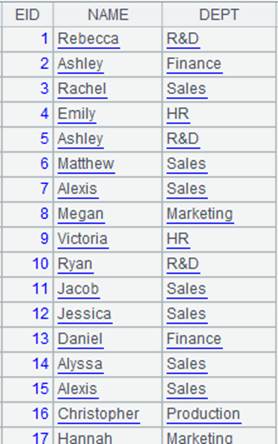
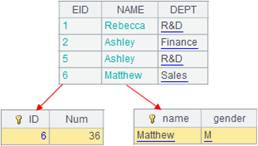
=create(file).record(["emp-fj.ctx"]) |
Below is content of composite table emp-fj.ctx:
|
|
2 |
=pseudo(A1) |
Generate a pseudo table from the composite table |
|
3 |
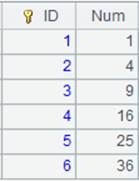
=6.new(~:ID,~*~:Num).keys(ID) |
Generate a table sequence whose primary key is ID
|
|
4 |
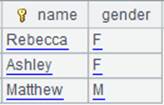
=create(name,gender).record(["Rebecca","F","Ashley","F","Matthew","M"]).keys(name) |
Generate a table sequence whose primary key is name
|
|
5 |
=A2.fjoin@i((EID=A3.find(EID),NAME=A4.find(NAME),EID!=null&&NAME!=null)) |
Define a computation on A2’s pseudo table, which will associate pseudo table A2 with A3 through foreign key field EID and with A4 through foreign key field NAME by switching EID to A3’s referencing records and NAME to A4’s referencing records, while deleting non-matching records in A2, and retrun a new pseudo table.
|
|
6 |
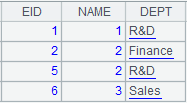
=A5.cursor().fetch() |
Fetch data from A5’s pseudo table while the computation defined on A2’s pseudo table in A5 is executed, and return the following pseudo table:
|
|
7 |
=A2.fjoin@i((EID=A3.pfind(EID),NAME=A4.pfind(NAME),EID!=null&&NAME!=null)) |
Define a computation on A2’s pseudo table , which will associate pseudo table A2 with A3 through foreign key field EID and with A4 through foreign key field NAME, by assigning ordinal numbers of the corresponding key values in A3 to A2’s foreign key field EID and assigning ordinal numbers of the corresponding key values in A4 to A2’s foreign key field NAME, while deleting non-matching records from A2, and return a new pseudo table.
|
|
8 |
=A7.import() |
Import data from A7’s pseudo table while the computation defined on A2’s pseudo table in A7 is executed, and return the following pseudo table:
|
When using other syntax:
|
|
A |
|
|
1 |
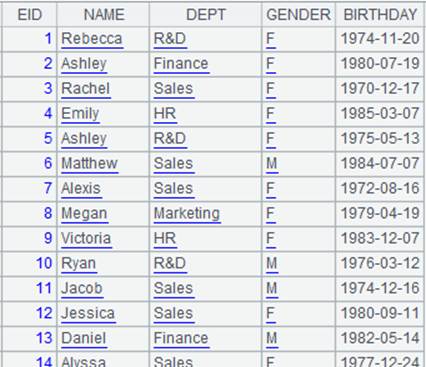
=create(file).record(["emp-fj2.ctx"]) |
Below is content of composite table emp-fj2.ctx:
|
|
2 |
=pseudo(A1) |
Generate a pseudo table from the composite table |
|
3 |
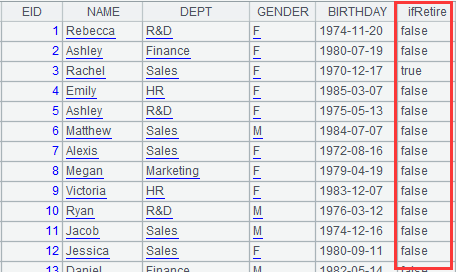
=A2.fjoin(age(BIRTHDAY):age,age>50:ifRetire) |
Define a computation on A2’s pseudo table, which will get age of each employee in pseudo table A2 – use age as the alias of age computation, find if each age is above 50, and add results of computing expression age>50 to pseudo table A2 as a new field named ifRetire, and return a new pseudo table:
|
|
4 |
=A3.cursor().fetch() |
Fetch data from A3’s pseudo table while the computation defined on A2’s pseudo table in A3 is executed, and return the following pseudo table:
|
|
5 |
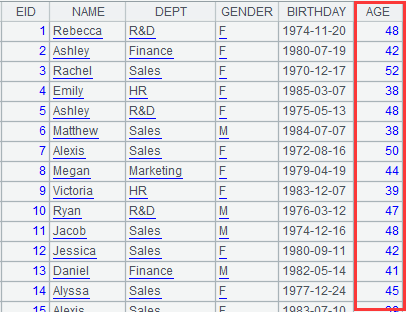
=A2.fjoin(age(BIRTHDAY),~:AGE) |
Define a computation on A2’s pseudo table, where parameter x represented by ~ means parameter w itself, that is, AGE field contains results of computing age(BIRTHDAY), and return a new pseudo table. |
|
6 |
=A5.import() |
Import data from A5’s pseudo table while executing the computation defined in A5 on A2’s pseudo table, and return the following pseudo table:
|
|
|
A |
|
|
1 |
=create(file).record(["emp-fj2.ctx"]) |
Below is content of composite table emp-fj2.ctx:
|
|
2 |
=pseudo(A1) |
Generate a pseudo table from the composite table |
|
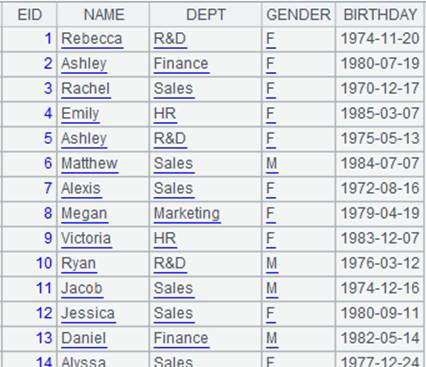
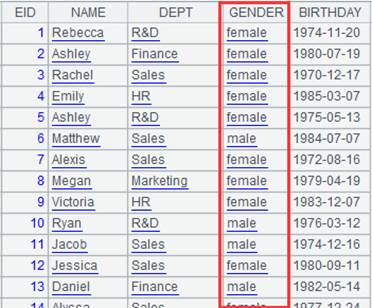
3 |
=A2.fjoin(if(GENDER=="F","female","male"):GENDER,GENDER) |
Define a computation on A2’s pseudo table – parameter w is the value assignment format; return female when GENDER value is F, otherwise return male; since w’s alias GENDER already exists in the pseudo table, the function won’t generate a new field but assigns new values to the GENDER field – and return a new pseudo table.
|
|
4 |
=A3.import() |
Import data from A3’s pseudo table while executing the computation defined in A3 on A2’s pseudo table, and return the following pseudo table:
|
|
|
A |
|
|
1 |
=create(file).record(["cities-x.ctx"]) |
Below is content of composite table cities-x.ctx:
|
|
2 |
=pseudo(A1) |
Generate a pseudo table from the composite table |
|
3 |
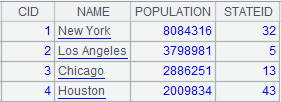
=A2.fjoin@i(CID<5) |
Define a computation on A2’s pseudo table, which will use @i option to get records of pseudo table where CID is less than 5 while deleting the whole record when computing result is null or false.
|
|
4 |
=A3.import() |
Import data from A3’s pseudo table while executing the computation defined in A3 on A2’s pseudo table, and return the following pseudo table:
|