1.9.2 Basic uses
In the cellset code, the result set is returned by return statement.
|
|
A |
|
1 |
=connect("demo") |
|
2 |
=A1.query("select * from EMPLOYEE where EID=?",arg1) |
|
3 |
>A1.close() |
|
4 |
return A2 |
In the application code, arg1 is a cellset parameter. Let’s name this script file test.splx.
Note: The result set of a script file is returned by return statement. When the script file is called, its parameters will get assigned in the order of their appearance, rather than according to the names.
1) Load the necessary jars. Load the basic esProc JDBC jars mentioned above while launching the Java application. These jars can be put in the directory of WEB-INF/lib under the web application.
2) Deploy raqsoftConfig.xml and script files.
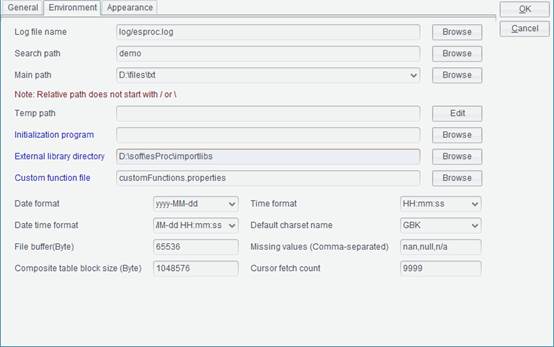
Configure the raqsoftConfig.xml file, which contains the basic configuration information of esProc, such as search path, data source configuration, etc. The file can be found in the path esProc\config in esProc’s installation directory and has the same information as that set in the esProc Option tab. The configuration is allowed to be adjusted before deployment (like modifying the Search path used to search for a script file):
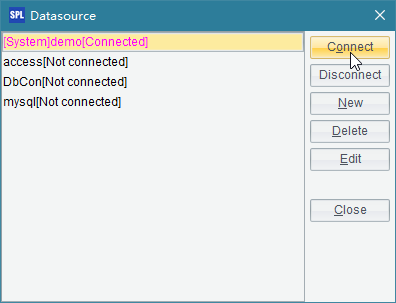
The data source used in a script file can be configured in the Datasource Manager:
After the modification, put raqsoftConfig.xml in the class path of the application that will use them.
Put the test.splx created in Step 1 in the class path of the application, or put it in the path specified by <splPathList/> node in the configuration file (i.e. the above-mentioned search path).
3) Further configure file raqsoftConfig.xml manually if necessary. For more details, refer to related documents. Note that the configuration file name must not be changed.
4) Call the script file in Java program.
public void testDataServer(){
Connection con = null;
java.sql.PreparedStatement st;
java.sql.PreparedStatement st2;
try{
//establish a connection
Class.forName("com.esproc.jdbc.InternalDriver");
con= DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:esproc:local://");
//call the stored procedure in which test is the name of the script file
st =con.prepareCall("call test(?)");
//set the parameters
st.setObject(1,"3");
//the result obtained by executing the following code is the same as that obtained using the above calling method
st =con.prepareCall("call test(3)");
//execute the stored procedure
st.execute();
//get result set
ResultSet set = st.getResultSet();
}
catch(Exception e){
System.out.println(e);
}
finally{
//close the connection
if (con!=null) {
try {
con.close();
}
catch(Exception e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
}
}
}
To learn more about the calling methods and configuration, please refer to Integration & Application.